Loading
Since modern data platforms converge toward the Cloud & the Lakehouse architecture, what are the differentiators? Which one is the best for you?
You are in the process of selecting a data platform, or you would like to modernize your data warehouse, data lake we have compared Microsoft Fabric, Databricks and Snowflake, here are the 4 main differences we have found:
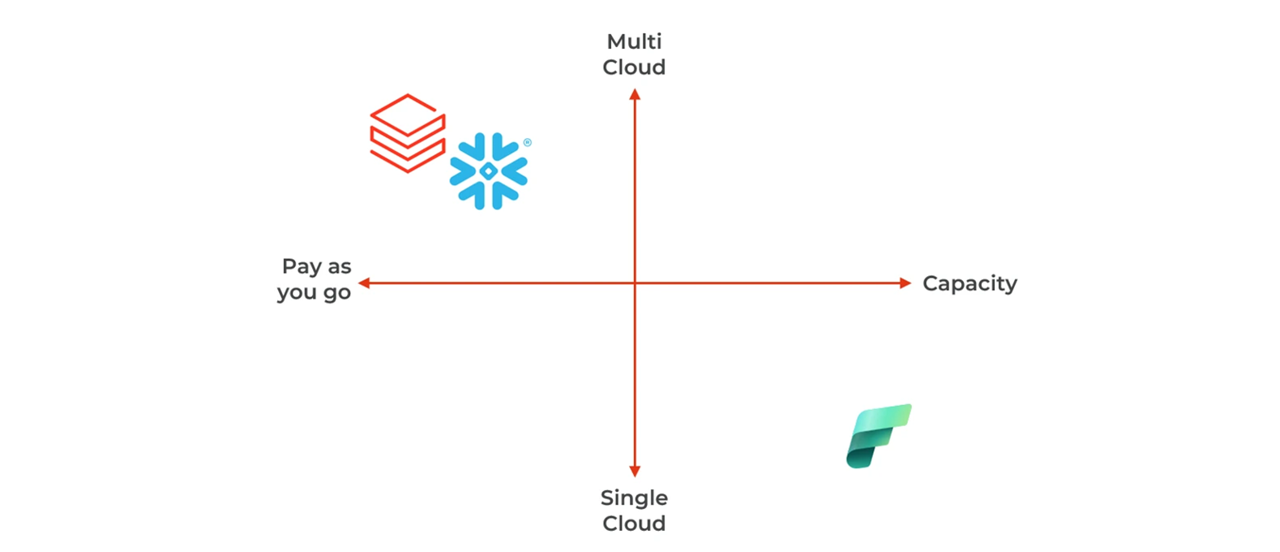
Availability and pricing differences
Whether you are cost sensitive, or have some existing Cloud strategy, or sovereignty requirements, you must choose the cloud and price model that fits:
- Fabric is only available on Azure and is based on a capacity pricing model.
- Snowflake and Databricks are pay-as-you-go with optional reservation, they are on the 3 main hyperscalers.
- Databricks is also available on SAP Business Data Cloud.

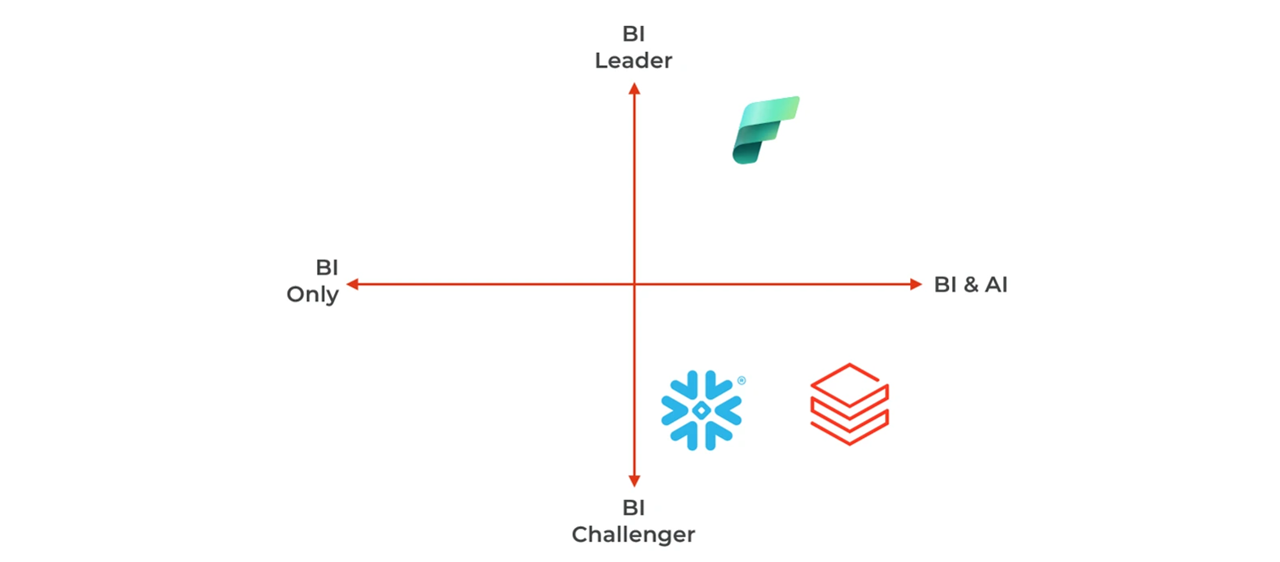
Data usage & consumption differences
You may start with BI requirements, still you are also interested by machine learning and GenAI for new use cases. Which platform has the best potential?
- Fabric’s Power BI is the leader in BI. Snowflake and Databricks are challenging this status with lighter dashboards. Databricks with Databricks One and Snowflake with Snowflake Intelligence push AI-powered UIs that open the platform to business users. Those products are competing with Fabric Copilot.
- All three platforms are investing heavily in GenAI. Databricks has recently announced Agent Bricks, a product that helps companies build their domain-specific agents

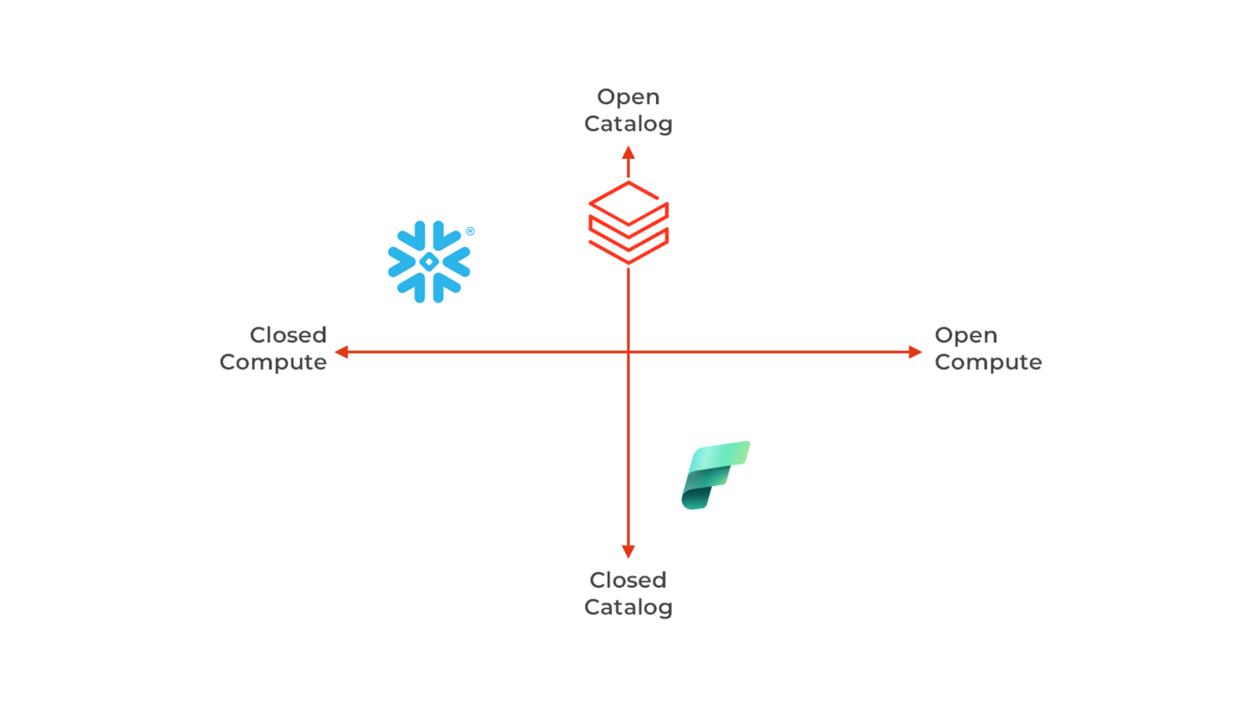
Interoperability and resilience through Open Standards support
Transitioning to or from a data platform is significantly influenced by open standards promoting interoperability. The ability to ingest and export data is crucial, meaning that open data formats are essential to support strategic orientations:
- Databricks supports many open-source technologies (Apache Spark, MLFlow, Delta Lake, Unity Catalog) but also some new proprietary ones (Delta Live Table, Lakeflow, Mosaic AI…). Databricks is now fully supporting Iceberg as an alternative to Delta Lake.
- Fabric is also a promoter of Spark, MLFlow and Delta. Other features are closed source (Power BI, Onelake, Warehouse…)
- Snowflake has opened its architecture through strong support for Iceberg tables, and open-sourced Polaris catalog. The main engines and frameworks remain closed (Warehouse, Snowpark, Cortex…).
- All are moving toward database management system supporting transactional workloads and AI applications: Databricks announced Lakebase, a managed Postgres, similarly Snowflake has a managed Postgres following the acquisition of Crunchy Data, Fabric integrates managed Azure SQL through Database Mirrors.

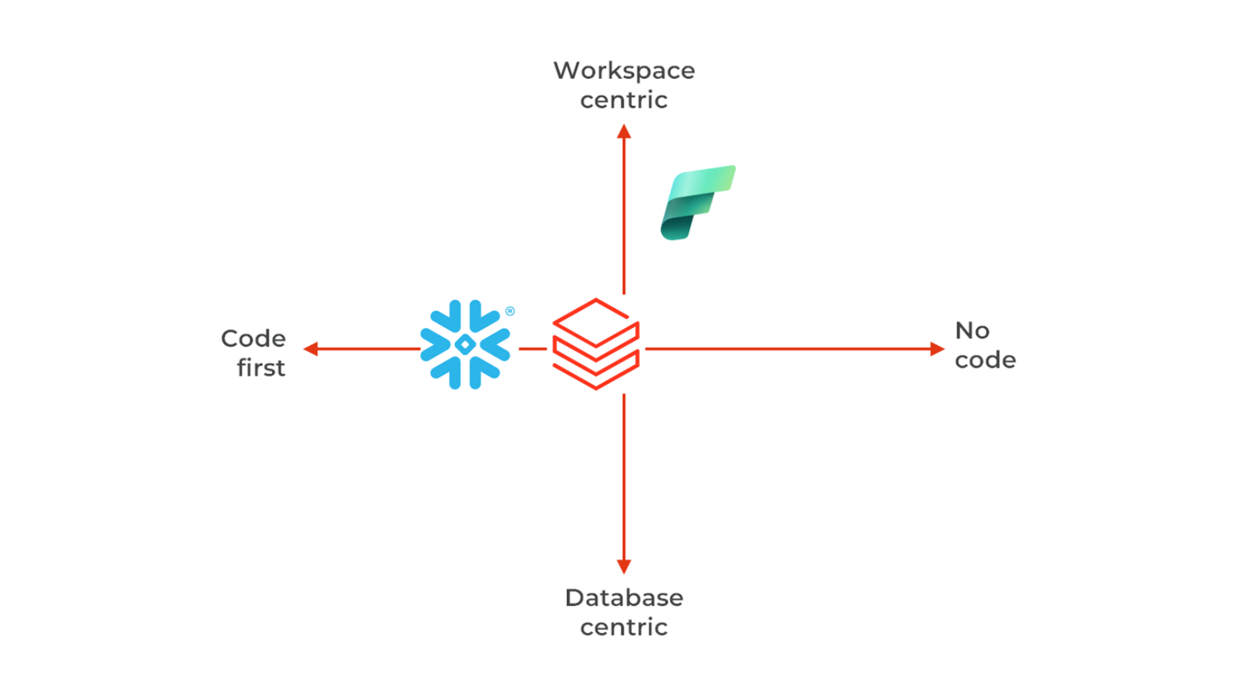
Code development and collaboration differences
This is likely the most complex — yet one of the most important — aspects to evaluate: how are developers and users interacting with the platform? Does it provide a user-friendly environment for data analysts, data engineers, data scientists, or all of them? Is it possible to collaborate within a Scrum team (7 people), or even larger teams like in SAFe setup? The answer has direct implications for staffing, onboarding, and broader organizational acculturation.
- Snowflake has a clean from the ground-up construction with everything declared as code into the catalog using SQL or Python. All code is versioned in GIT. In Snowflake collaboration is within Workspaces, and artifacts (tables, AI models…) are stored in Databases.
- Fabrics is expanding the Power BI organization of objects in Workspaces. Versioning is JSON declarations, one repository per Workspace.
- Similarly to Snowflake, Databricks has Workspaces (single workspace per session), managed assets in Unity Catalog (schema, tables, volumes, AI models). The Workspace assets (compute, dashboards, notebooks…) are deployed through Asset Bundles. Versioning is a mix of Python/SQL code and JSON declarations.
- Moreover, Snowflake and Databricks today offer some low-code ETL, i.e. Snowflake OpenFlow and Databricks Lakeflow Designer.

Get a free 30-minute call with our expert !
You are in the process of selecting a data platform, or you would like to modernize your data warehouse, data lake, contact us and get a free 30-minute call with our expert.
Contact our Expert
Antoine Hue
Data Architect
Introducing Antoine Hue our data expert. Antoine is a data architect for the data migration and analytics platforms, and he is responsible for the data engineering team in Romandie.

Subscribe to our Data & AI Newsletter!
Subscribe now and stay one step ahead in a world where data, analytics & AI are transforming every industry.
